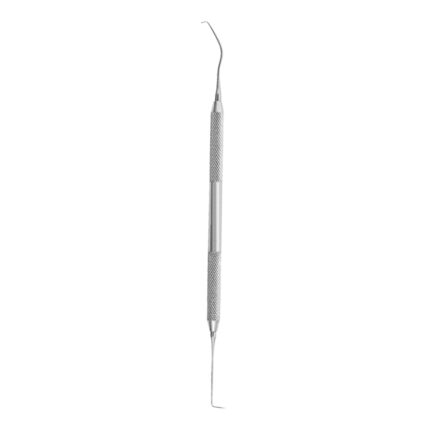
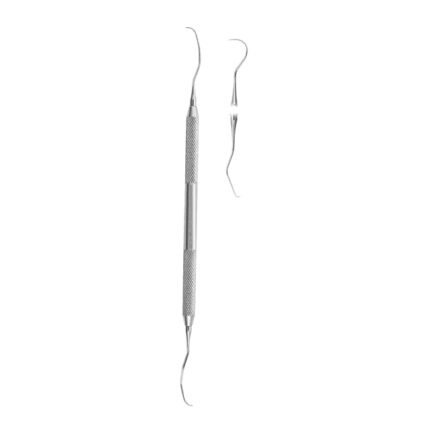
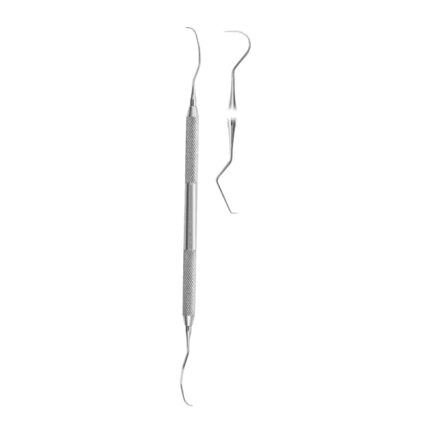
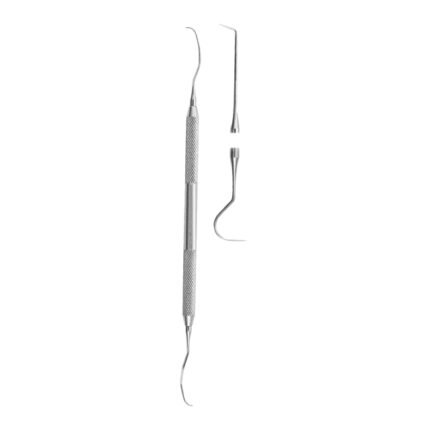
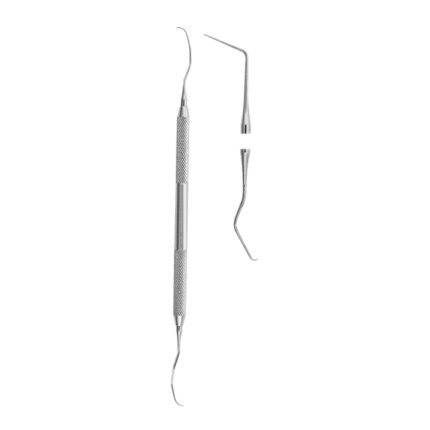
Double-Ended Explorers are dental instruments designed to help dental professionals detect cavities assess the condition of restorations
- Surgical Instruments
- Beauty Instruments
- Barracuda Hair Scissors
- Blue Coated Scissors / Shears
- Cuticle & Personal Care Scissors
- Cuticle Nippers
- Cuticle Pushers
- Economy Hair Scissors
- Economy Hair Thinning Scissors
- Hair & Skin Care Tools
- Hair Care Sets
- Hair Cutting & Thinning Scissors
- Hair Cutting Scissors
- Hair Extension Pliers & Kits
- Leather Shears Pouches Empty
- Manicure & Pedicure Implements
- Manicure & Pedicure Kits
- Multi Color Shears
- Nail & Pedicure Cutters
- Pedicure & Nail Care Tools
- Plastic Handle Shears
- Professional Hair Cutting Shears
- Professional Razor Edge Shears
- Professional Tweezers
- Cut Hair Scissors
- Titanium Coated Hair Scissors
- Dental Instruments
- Amalgam Carriers
- Amalgam Carvers
- Articulators
- Bone Files
- Cavity Preparation Instruments
- Cement Spatulas
- Combination Explorers Probes
- Crown Instruments
- Dental Retractors
- Dental Scissors
- Double-Ended Explorers
- Endodontic Instruments
- Excavators
- Explorers
- Explorers Anatomic Handle
- Extracting Forceps
- Filling Instruments
- Gracey Curettes
- Heidemann Sparating Spatulas
- Implant Surgery
- Laboratory Instruments
- Laboratory Tweezers
- Matrix Retainers
- Needle Holders
- Periodonral Instruments
- Periodontal Instruments
- Periodontial Pocket Probes
- Plaster Alginate & Elastomers
- Pliers
- Retractors Tongue Depressors
- Root Elevators
- Rubber Dam Clamps
- Saw & Blades
- Scalers
- Scalpel Handles / Blades
- Surgical Saliva Ejectors
- Syringes
- Towel Clamps
- Trays
- Wax & Modeling Carvers
- Root Tip Picks
- TC instruments
- Ophthalmic Instruments
- Orthopaedic Instruments